Hip Fracture VDO Project – Our Experience And Outcomes
Case study
Background
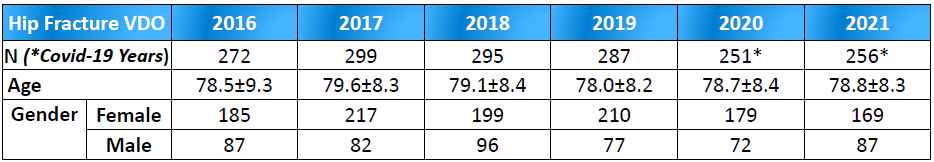
Hip fracture literature has shown the clinical effectiveness of Care Pathways. However, there remains a paucity of knowledge on the collaborative exchange on best practices and the financial costs of providing hip fracture care between individual institutions. The Ng Teng Fong General Hospital's (NTFGH) Orthopaedic Surgery team had embarked on the hip fracture VDO project since 2017 by delivering safe and effective value-based care to our patients. Length of stay and expedited care during COVID-19 pandemic were key challenges as COVID surveillance swabs conducted on hip fracture patients prior to surgery would inadvertently create unintended delays in surgery.
Objectives
- To evaluate the value (quality and cost) of a defined patient cohort undergoing hip fracture surgery from 2016 to 2021.
- To assess how the COVID surveillance protocol has expedited surgery within 48 hours upon ED presentation despite COVID surveillance, by comparing patients who underwent hip fracture surgery on pre- and post-implementation of the COVID surveillance protocol.
Methodology
An all or none composite indicator, Clinical Quality Index (CQI) was computed to determine the proportion of patients which met all 7 clinical quality indicators.
Clinical Quality Indicators
- Surgery done ≤ 48 hours upon ED presentation
- Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis
- Osteoporosis Assessment
- Length of Stay ≤ 10 days
- (No) Mortality ≤ 30 days from admission
- (No) Readmission ≤ 30 days (all cause)
- (No) Unscheduled Return to OT ≤ 90 days (hip related)
COVID surveillance protocol implemented:
- COVID surveillance patients were started on the hip fracture clinical pathway and reviewed early within 24 hours by the Orthopaedic and Anaesthesia doctors.
- All patients had their COVID swabs done at 18 hours interval to meet 48 hours surgery timeline Patients were listed for surgery as soon as the second swab’s results were out.
- Patients were operated within the day of listing and within 48 hours.
Results
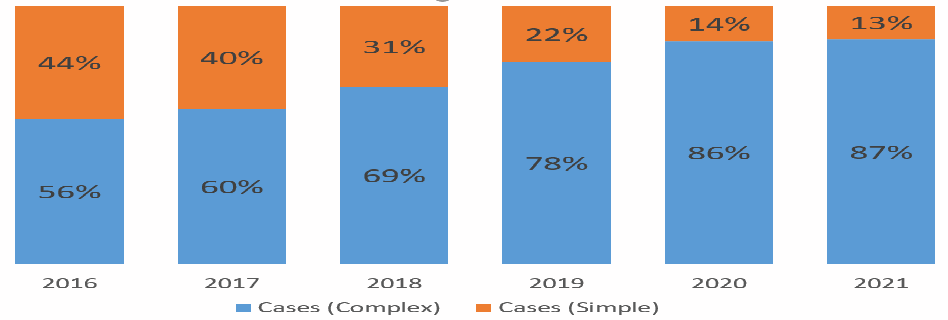
A total of 1,660 patients were included in the study. No significant differences in patient demographics were observed (p>0.05). However, the proportion of complex cases significantly increased by 46% in 2021 as compared to 2016 (p<0.05).
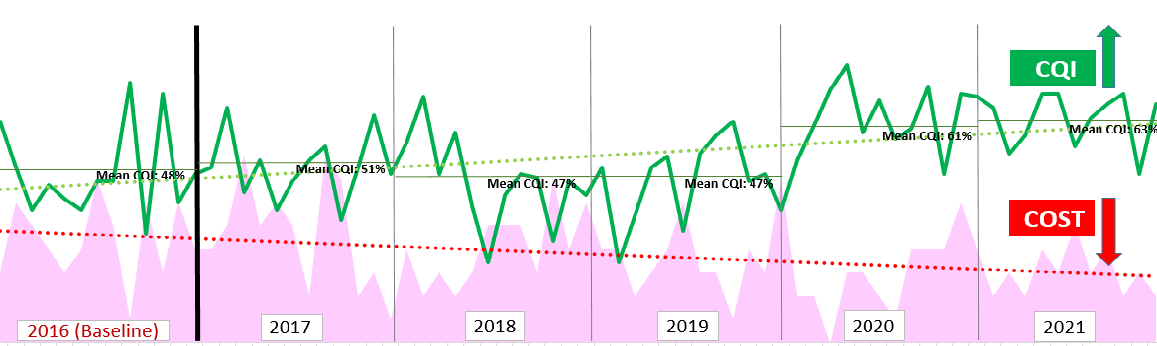
Comparing 2016 and 2021, the cumulative change in CQI increased by 27% (p<0.05) with a significant decrease in cumulative change in Cost by 8% (p<0.05) despite an increase in complexity and challenging COVID-19 pandemic in 2021.
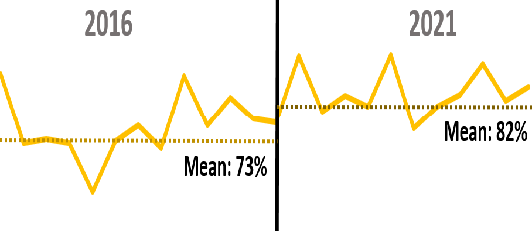
The proportion of patients with length of stay, 10 days increased significantly from 73% to 82% (p<0.05).
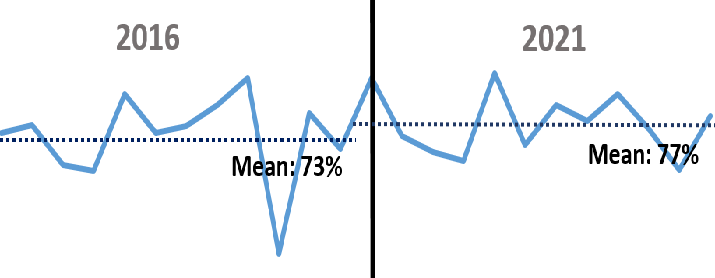
Surgery done in ≤ 48 hours upon ED presentation increased from 73% to 77% (p=0.37), whilst 30-Day readmission rate decreased by 3% (p=0.06).
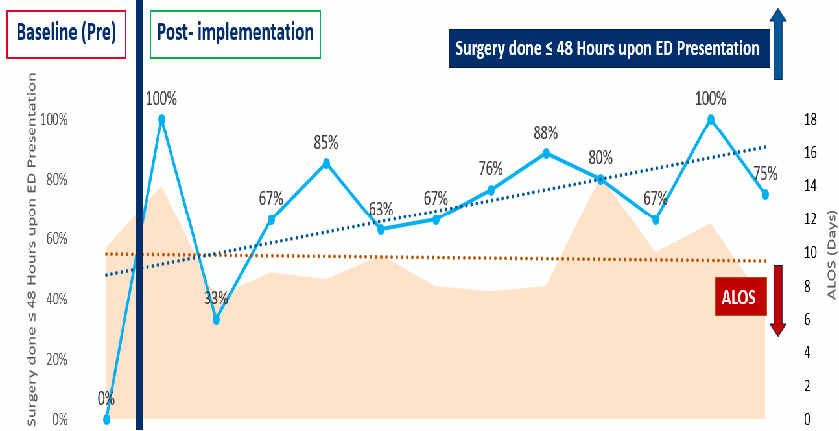
155 out of 300 patients who underwent hip fracture surgery from April 2020 to March 2021 were COVID surveillance patients. Surgery done within 48 hours upon ED presentation and average length of stay (ALOS) improved on post-implementation of COVID surveillance protocol.
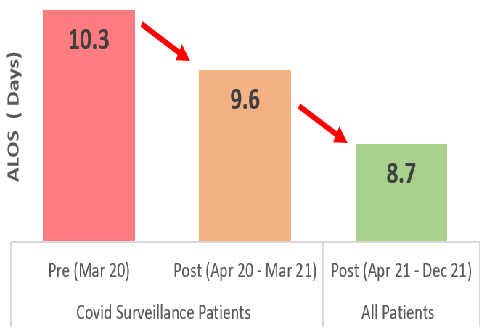
ALOS has decreased from 10.3 days to 9.6 days, and further improved to 8.7 days thereafter despite the surveillance swabs. (COVID surveillance patients had to stay an additional 2 days).
Conclusion
- Implementation of VDO has shown improved, sustained clinical outcomes and cost for hip fracture surgery despite significant increase in case complexity.
- The internalised COVID Surveillance Protocol improved patient outcomes reduced ALOS and costs.
- Strong leadership and support from the multidisciplinary team are essential to the continued functioning of hip fracture pathway.
























