The doctor will perform a thorough physical examination of your entire body, particularly the abdomen and the rectum. The skin, mucous membranes, eyes or joints will also be checked to assess for signs of inflammation.
The investigations may include blood tests and colonoscopy.
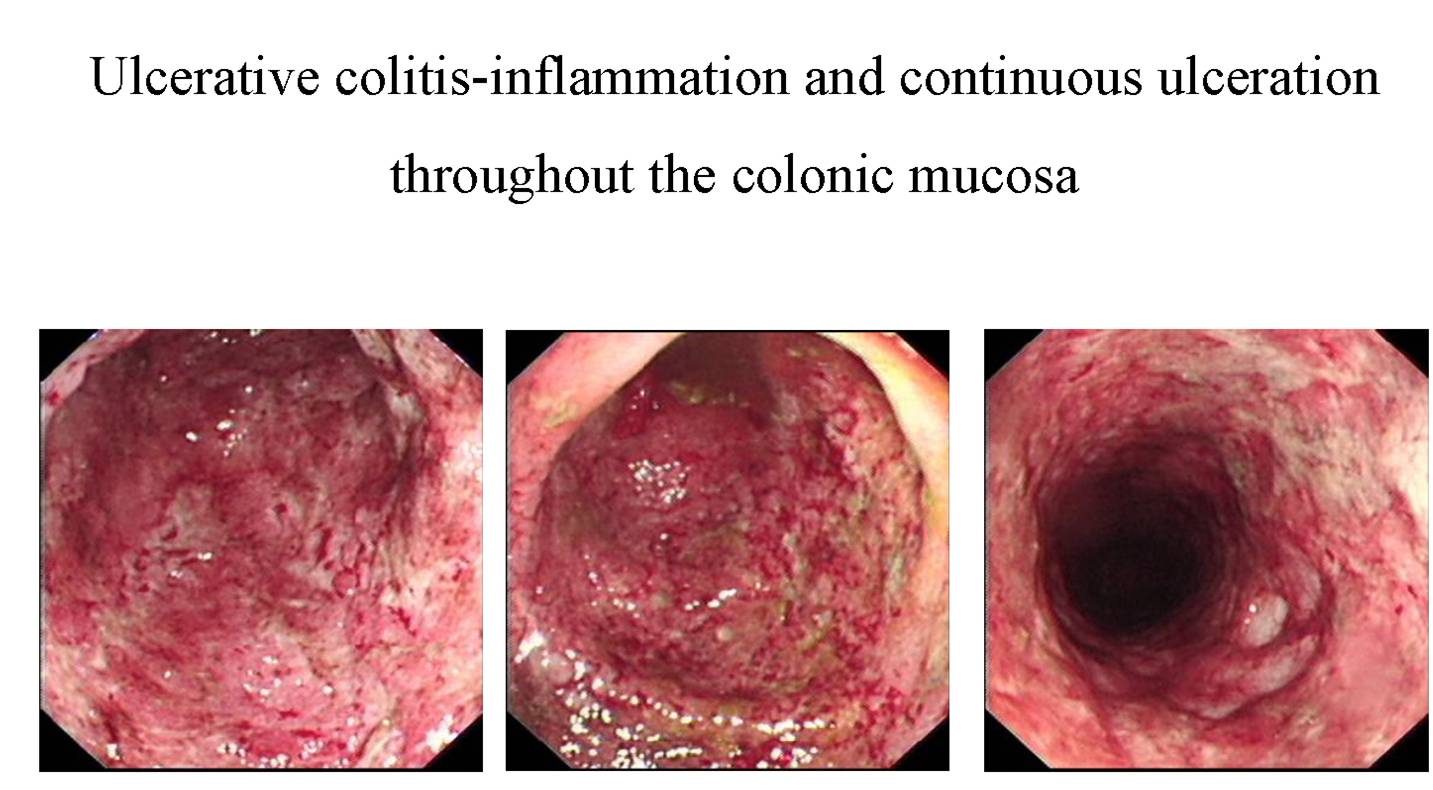
During the colonoscopy, tissue samples of the inflammed colon can be taken for further testing.
It is important for you to understand that UC is a chronic disease and can remain inactive with careful medical attention and ongoing monitoring.
There may be frequent visits to the doctor initially to bring the disease under control. Long-term monitoring is required.
















