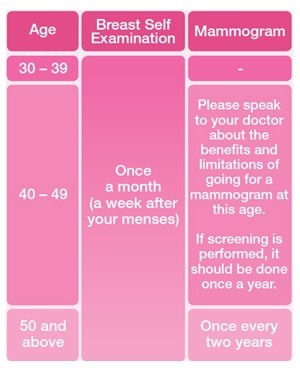
The female breast is made up mainly of:
- Lobules (milk-producing glands)
- Ducts (tiny tubes that carry the milk from the lobules to the nipple)
- Stroma (fatty tissue and connective tissue surrounding the ducts and lobules, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels)
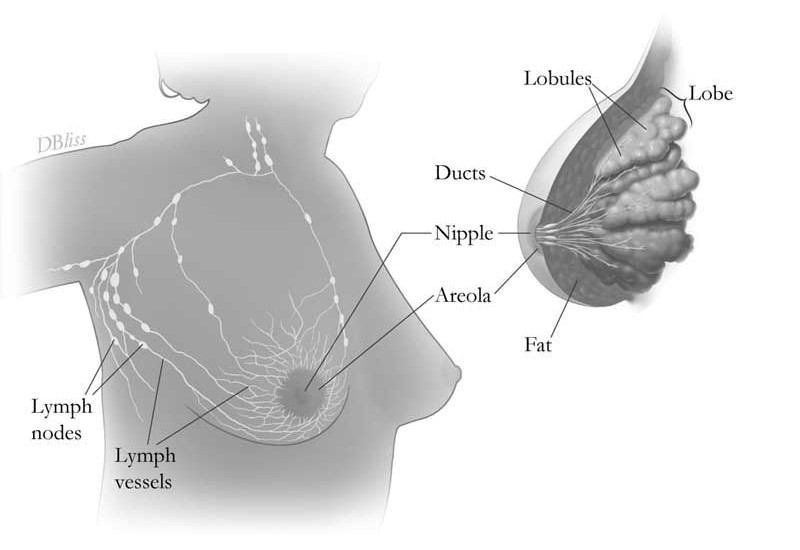
Breast Cancer is a group of cancer cells or malignant tumour that has developed from the cells in the breast. These cancer cells have grown into the surrounding tissues or spread to distant parts of the body. It usually starts in the cells of the lobules (the milk-producing glands) or the ducts (the passages that drain milk from the lobules to the nipple).
In other cases, this type of cancer can begin in the stromal tissues, which are the fibrous and fatty connective tissues of the breast.
It is the most common cancer in women and it can occur in men too. There are two broad types of cancer; the non-invasive Breast Cancer and invasive Breast Cancer.
The non-invasive Breast Cancer cells are contained within the milk ducts. However, if left untreated, the cancer cells can break out of the milk ducts and spread out, thus becoming an invasive Breast Cancer.
The invasive Breast Cancer cells spread outside the milk ducts or the lobules. These cancer cells will first spread to the surrounding breast tissue, move into the lymph nodes or blood stream and then travel to other parts of the body. The most common parts that the cancer cells travel to are the lungs, liver and bone.