There are many potential risks involved in a parathyroidectomy surgery. It is important to realise that whilst some of these risks are serious, they are relatively rare.
As with any operation, there may be some bleeding from the site of the operation.
The scar is usually sited within the skin crease. Most scars are more visible within the immediate post-operative period, but will be better camouflaged when the wound heals.
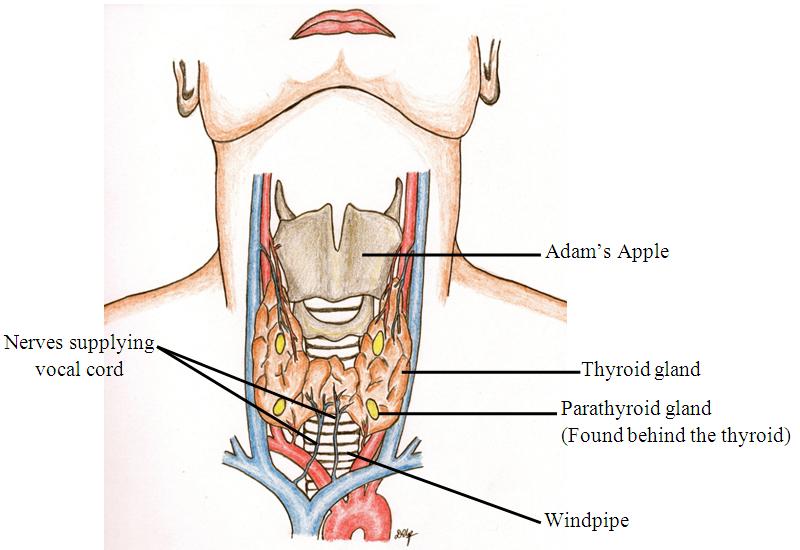
- Damage to recurrent laryngeal nerve
This nerve supplies the vocal cords. If one is damaged during the operation, the result may be a hoarse voice or a weak voice.
There can be low calcium levels following removal of a hyperactive parathyroid gland after surgery. Patients may need to take supplemental oral calcium for a few days to several weeks following surgery.
If there are persistently high calcium levels in the blood, there may be remnant parathyroid tissue either in the neck or other areas of the body. Further investigations or a second procedure may be required to find and remove the remaining parathyroid glands.